CLICK on each Question to open up the Answer below it.
For this “Start Here” page, it’s best to follow them in order (from top to bottom)
(Best viewed on a larger screen) / (Hyperlinks will open a separate tab with more info)
We know that light causes plants to grow, but how can light help the human body?
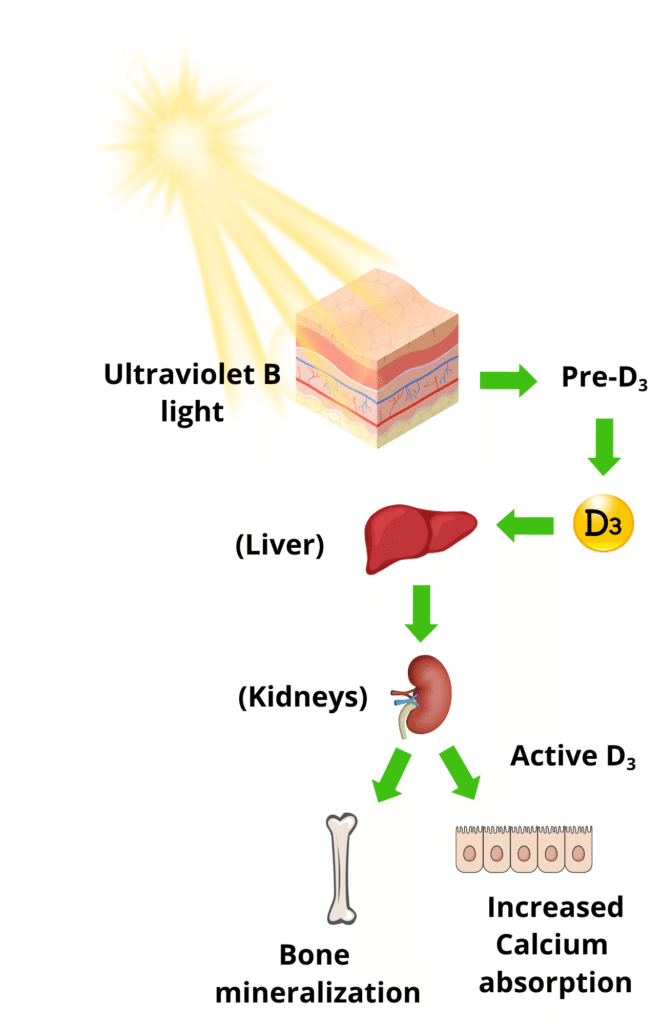
A simple example is when light from the sun helps the body make Vitamin D.
Sunlight (that includes Ultraviolet B light) shines on the skin and triggers the cells in our body to start the first step of Vitamin D “synthesis”.
There is no Vitamin D in the sun or in the sunlight, but the Ultraviolet B light signals the cells in the body to start making Pre-D3.
Then our body continues the rest of the process through the liver and kidneys until it finally gets Active D3 (a few days later) which helps maintain proper calcium levels and immune function.
NOTE: It was a certain kind of LIGHT (Ultraviolet B in this case) that started this process of making Vitamin D in the body.
What is light?
Light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye or other detectors.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
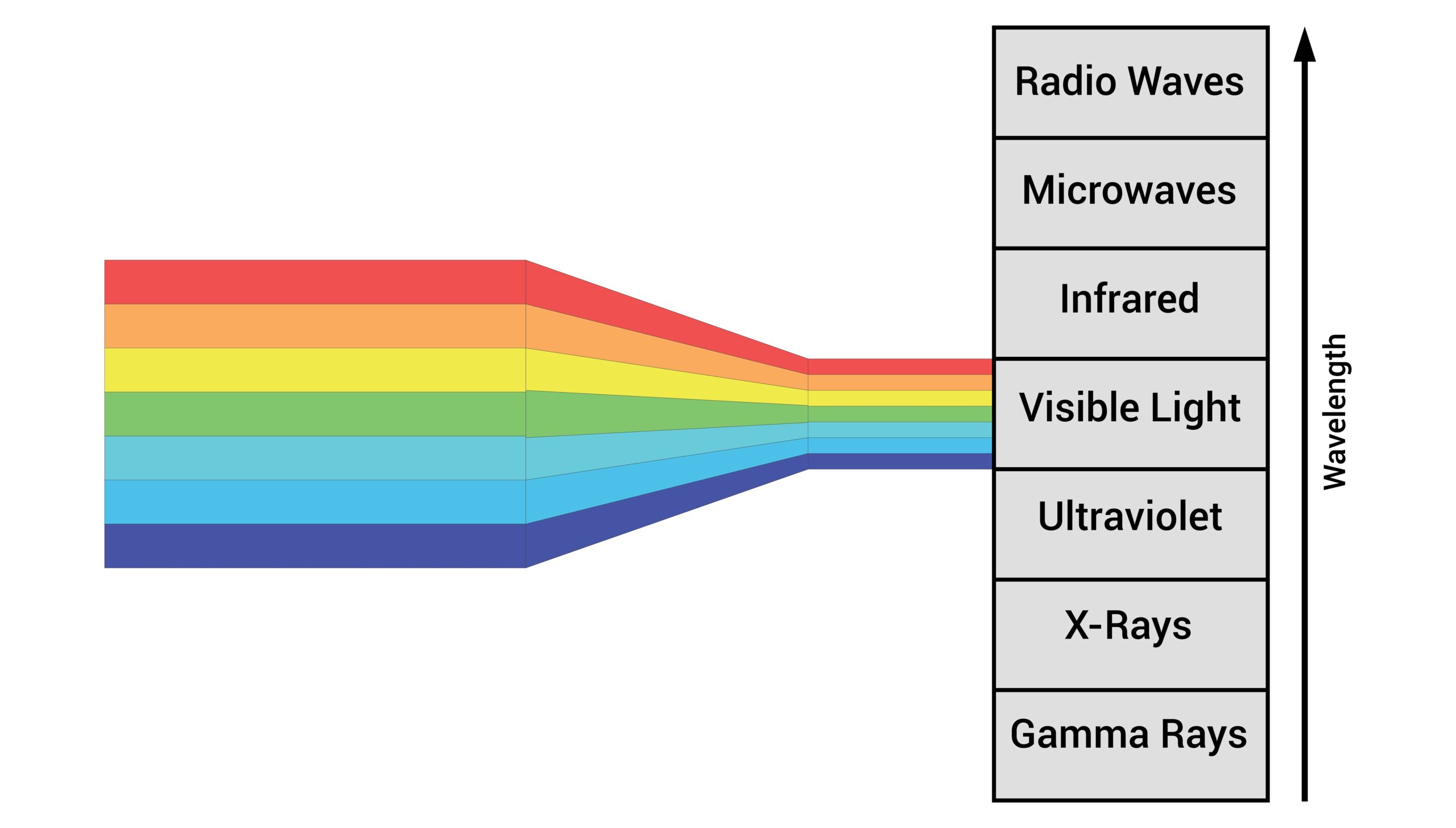
The Electromagnetic (EM) Spectrum shows all the different kinds of EM radiation (or light) we can measure.
The human eye can see only the visible part of the EM spectrum.
Visible light is EM radiation that has a wavelength between 400 nm and 700 nm.
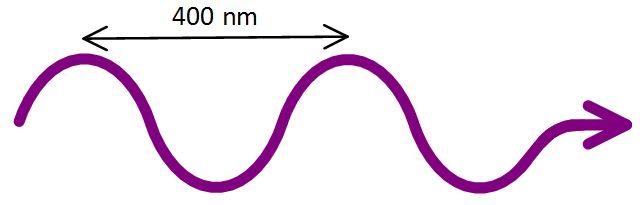
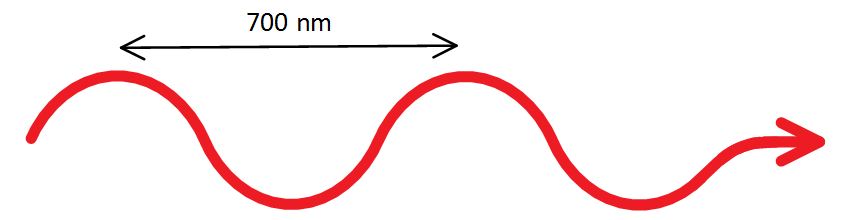
Note: nm stands for “nanometer” or 1 x 10-9 meters (that’s really tiny). Also, any wavelength of light can be converted to its frequency using the simple equation:
Speed of light (c) = wavelength (λ) / frequency (f)
What is light therapy?
Light therapy is a way to treat the body by shining light onto it.
Different kinds of light therapy (or phototherapy) include:
- Red light therapy (typically combines visible red and near infrared light)
- LLLT (Low-level Laser Therapy)
- UVB (Ultraviolet B) light therapy
- Bili light therapy (blue/green fluorescent light) – treats newborn Jaundice
- Heliotherapy (sunbathing)
- Sauna therapy (Far Infrared)
- PUVA (Psoralen Ultraviolet A) – treats skin conditions
Different kinds of phototherapy use different wavelengths (or frequencies) of light to help the body heal a certain way. “Photobiomodulation“ is another term used to describe phototherapy because the light initiates biological changes.
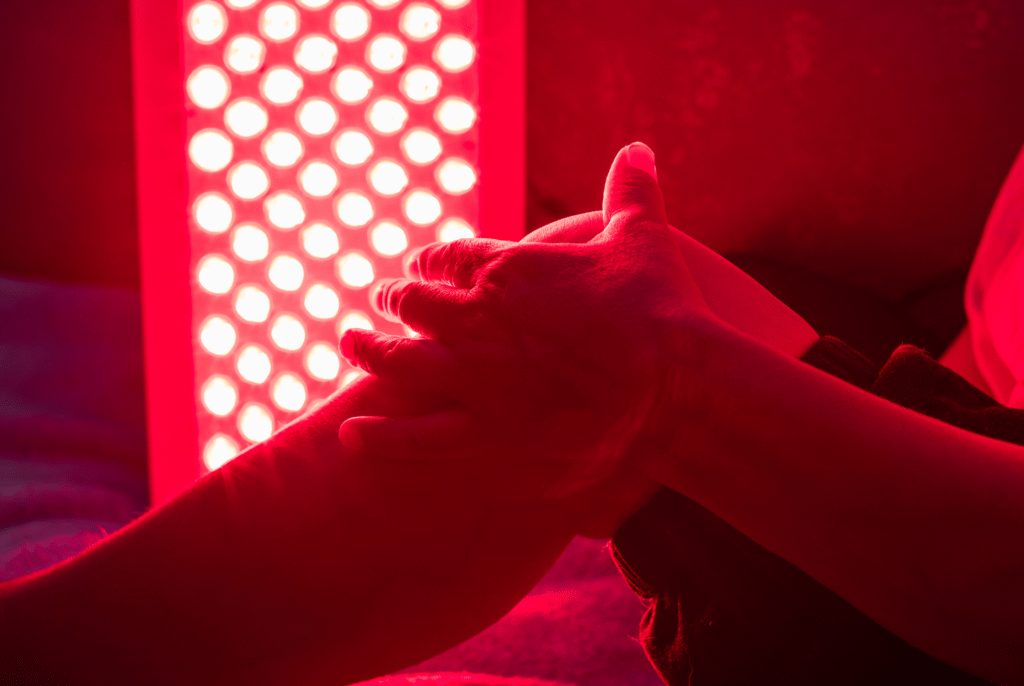
What is Red light therapy?
Red light therapy shines red light directly onto the skin.
Laser medical treatments like Red Light Therapy (RLT) have been in use since 1967 (when a Helium-Neon laser was first used to accelerate wound healing). More recently, RLT has become a common at home therapy because of the low cost of LED light compared to laser light.
RLT typically uses certain wavelengths of visible red light along with near infrared light. The 610 nm, 630 nm, 660 nm, 810 nm, 830 nm, & 850 nm wavelengths have been used to help the body in a number of ways. Of these, the 660 nm and 850 nm wavelengths are the most widely used in RLT devices.
For example, when 660nm light is absorbed by cytochrome c oxidase (a key enzyme in mitochondria in your cells), it starts off a number of processes in the body:
- Increases ATP production (More cellular energy for repair and creating stronger new cells)
- Reduces oxidative stress (Lowers inflammation and speeds up healing)
- Stimulates collagen & elastin (Improves skin health and reduces wrinkles)
- Increases blood circulation (Promotes faster recovery and pain relief)

What are Lifewave patches?
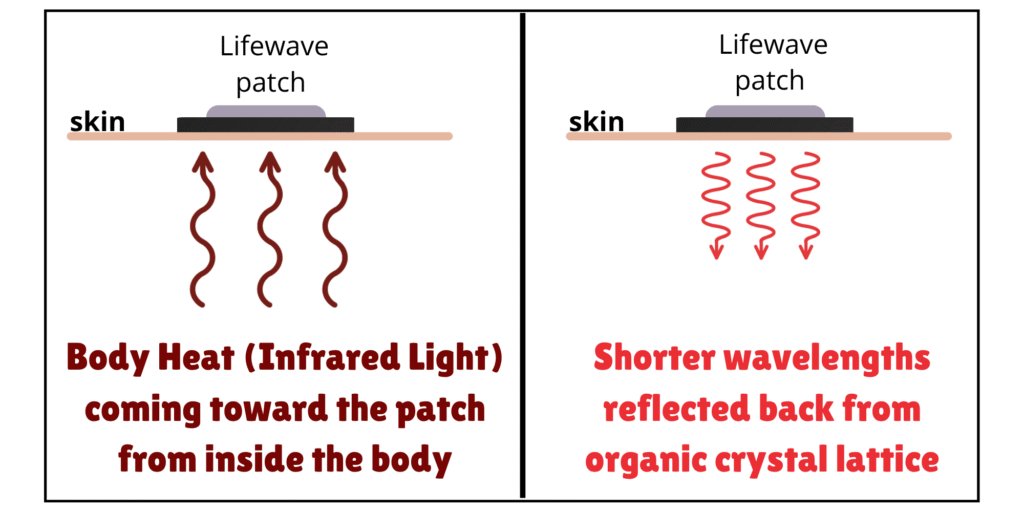
Lifewave patches are a very unique kind of phototherapy. All other types of phototherapy use an external light source (laser, LED, sunlight) to send light waves to cells in the body to initiate certain chemical reactions (photobiomodulation).
Lifewave patches use infrared light from the human body and reflect it back to the body after the wavelength is adjusted by an organic crystal lattice (made of salts, sugars, and amino acids). The nano-scale crystals are made to a precise size and spacing in order to reflect back specific wavelengths of infrared and visible light (different wavelengths for different patches).
Here are some more details:
An Infrared camera can “see” the infrared light (or body heat) coming off of a person.
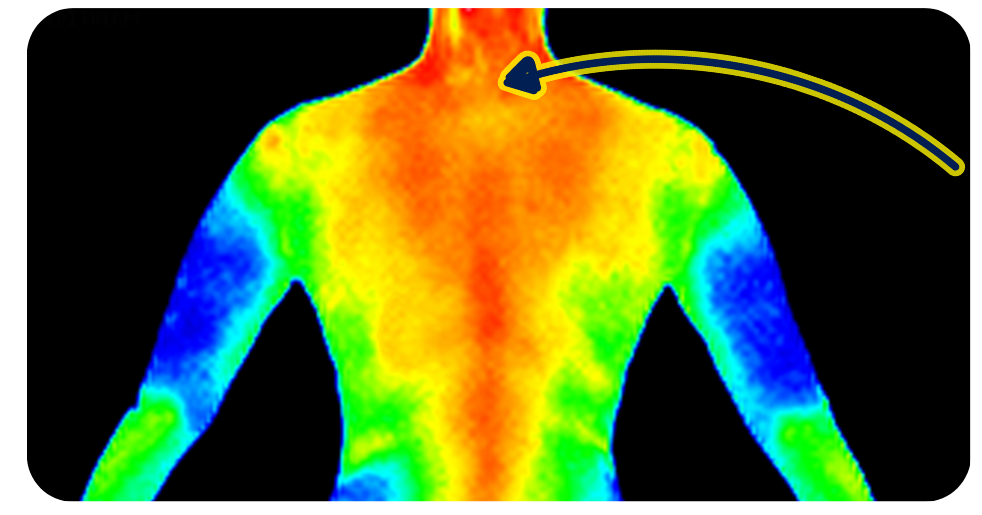
The back of the neck is a typical place to put a patch because there are a number of nerve bundles there.
Below you can see it at the same location (on the back of the neck).
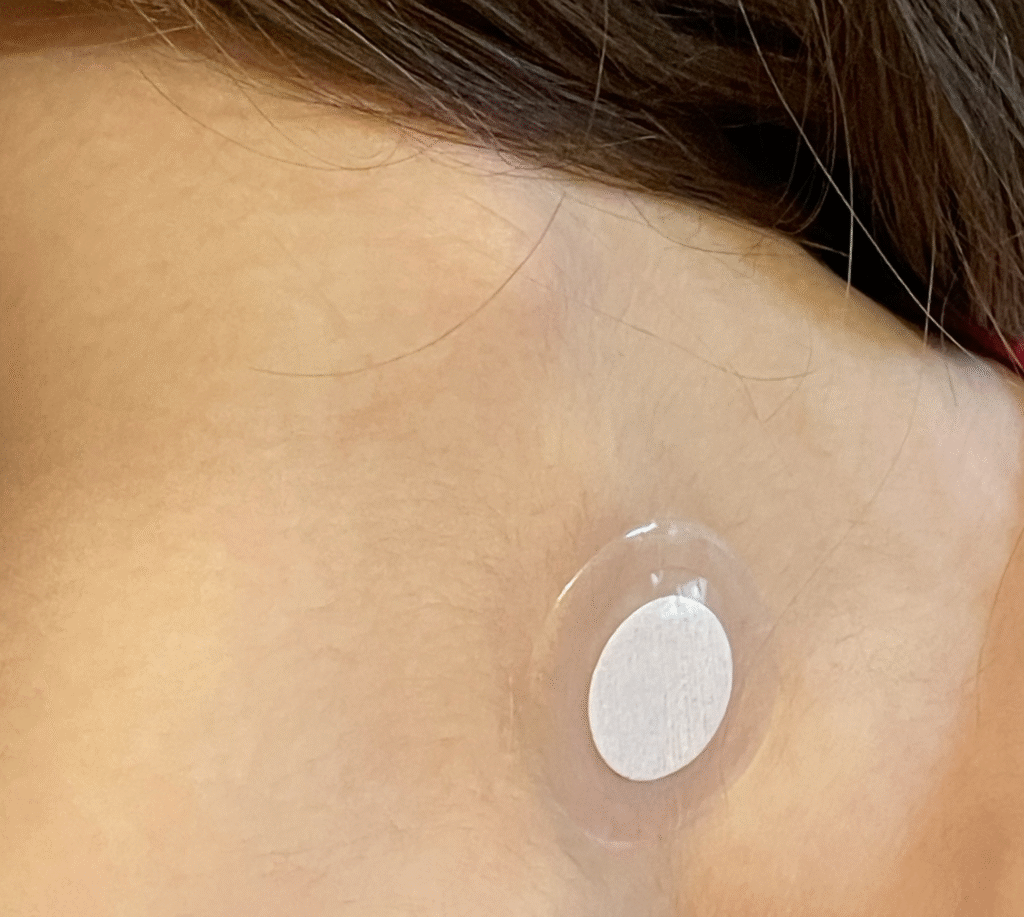
Here is the same scenario but looking at it from the side.

What are Lifewave patches made of?

The mixture of salts, sugars, and amino acids are absorbed into a polyester gauze and then slowly dried (using pH to control crystal size).
The patches are enclosed in plastic (on both sides) and are “non-transdermal” meaning they do not transmit any chemicals to the skin. There is latex adhesive on one side so it can stick to skin or clothing (it doesn’t have to be put on the skin, just at most 1 inch away from the body).
*See the lists of ingredients here
*For more detailed ingredients and their concentrations, you can look at the most recent patent update (jump to pages 26 -33)
How do Lifewave patches help the body?
(Follow the pictures below)
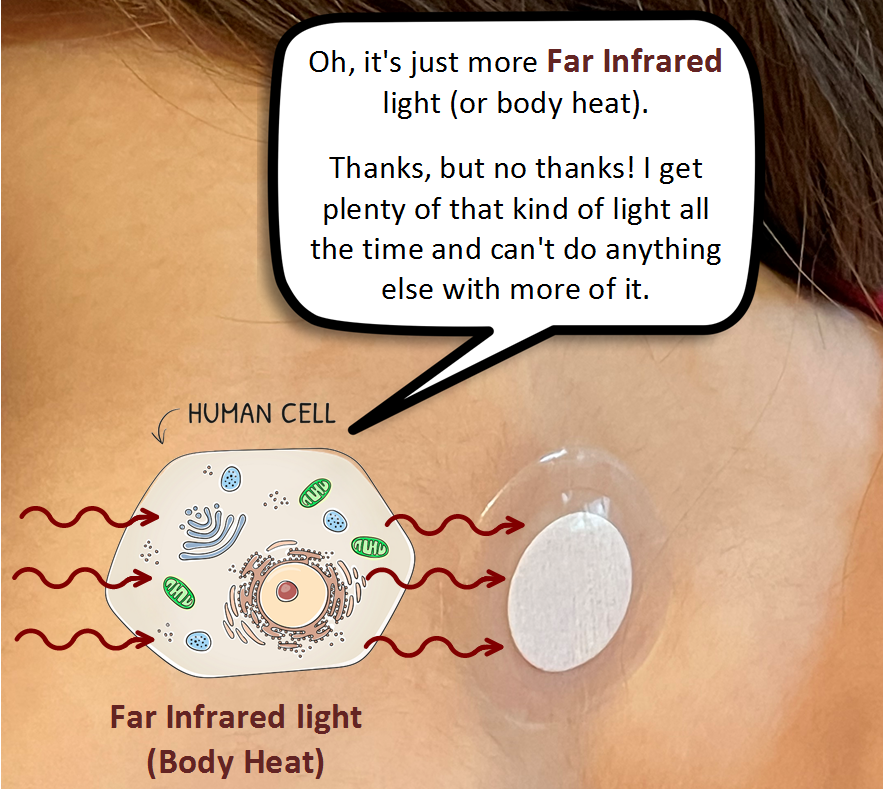
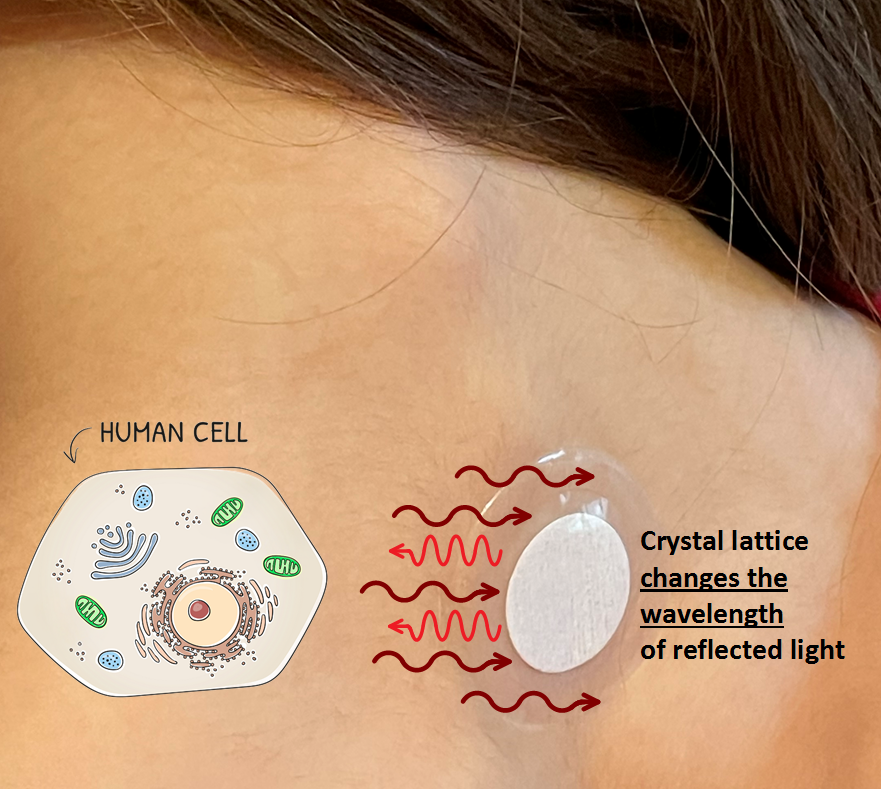
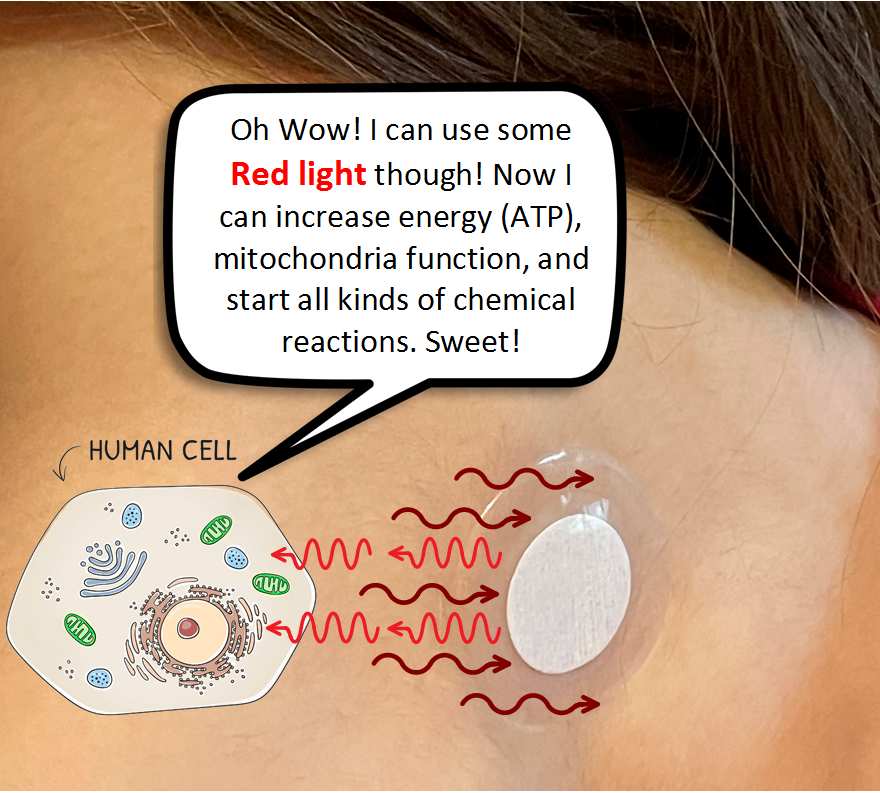
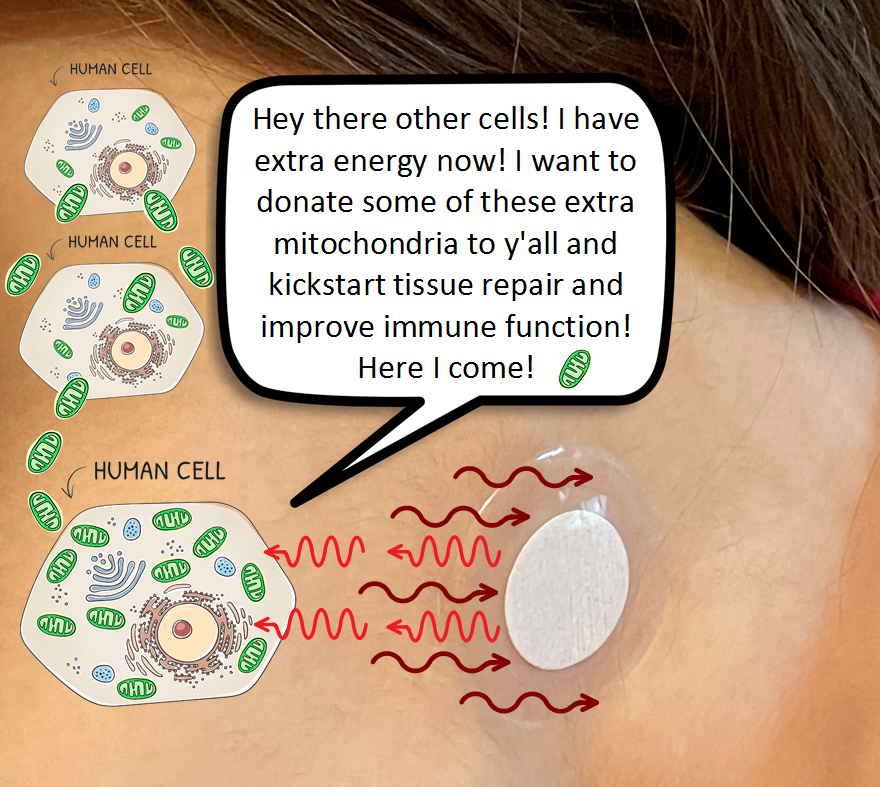
This sequence above is just one example when “broadband” Far Infrared light is reflected back to the body (or modulated) as “narrowband” Visible and Near Infrared light. Specific wavelengths of Red light (630 nm, 660 nm) are well known for increasing mitochondria function and starting a number of beneficial chemical reactions.
Lifewave patches are unique because they absorb and emit a wide array of wavelengths in the range of 600 nm – 4600 nm (compared to only a few wavelengths for red light therapy) US Patent No. 12220599-B2 — see the bottom right of page 35 (out of 37) that describes the results of the Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (see Figure 12 on page 14 for graphical results).
Lifewave has developed patches that signal specific peptides for increasing stem cell activity (biggest breakthrough), reducing inflammation and pain, raising glutathione levels without any supplements, healing injuries more quickly, etc. all through using light. This is basically regenerative medicine via light.
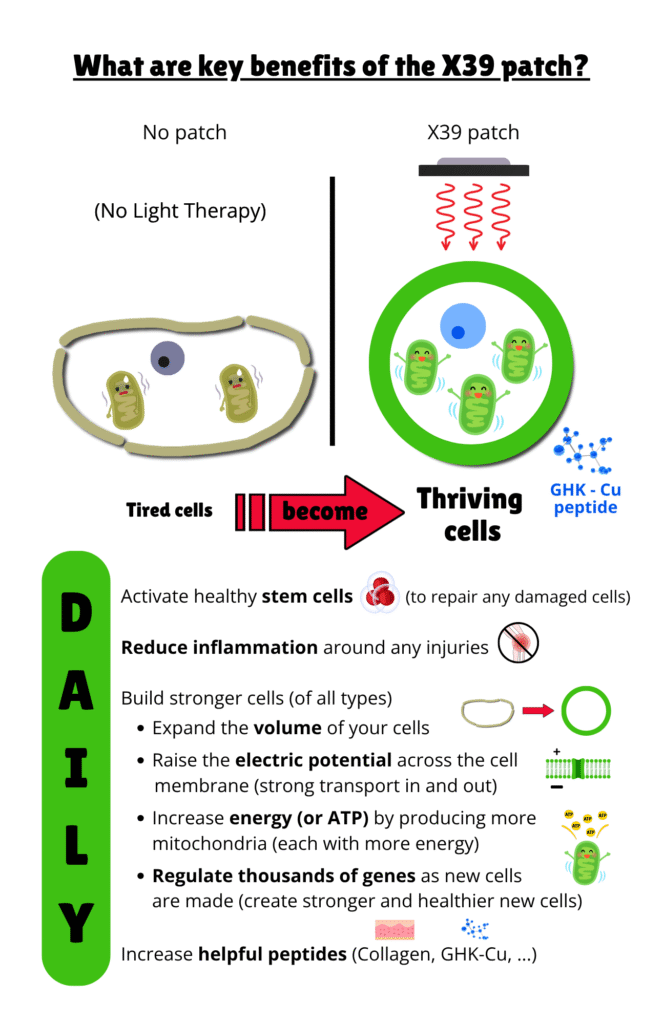
What are the benefits of wearing the X39 patch and how long until I see or feel any effects?
You may feel something significant within the first week or month, but you may not. Your body heals what it sees as most critical first and that may not be something you can necessarily feel (like the lining of your arteries, an organ, or scar tissue repair).
Click here for a list of benefits overtime. Check out the X39 clinical studies to see specific effects measured in the body.
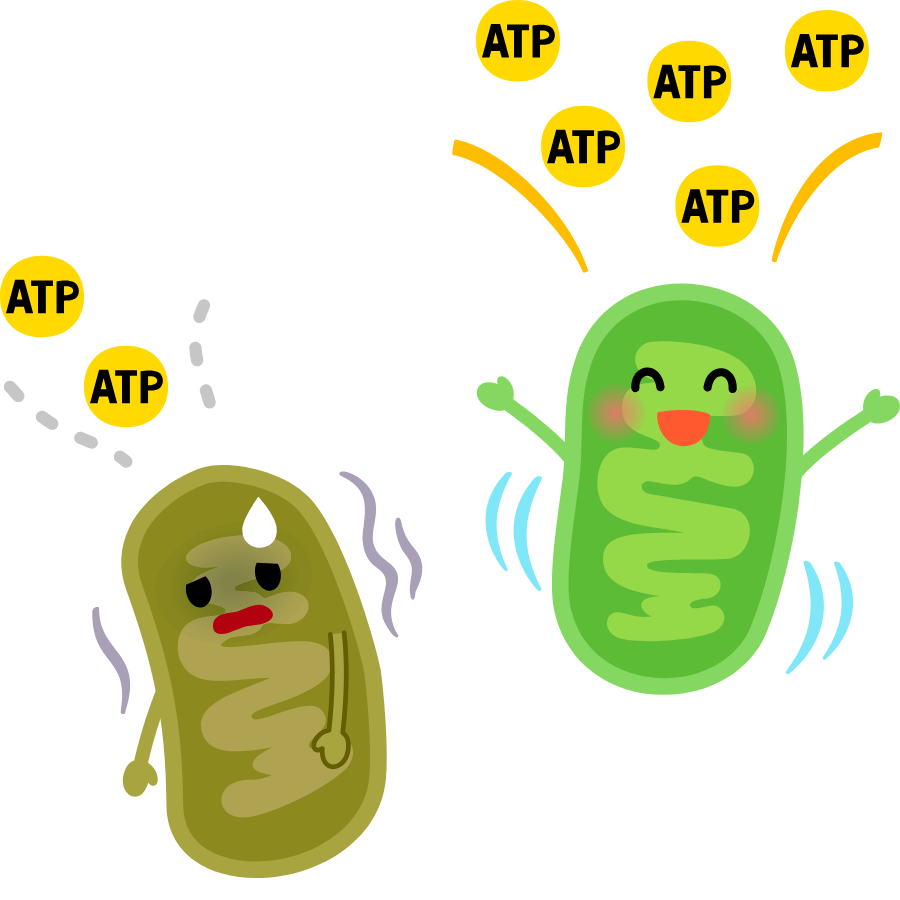
How do the patches “modulate” or adjust the incoming infrared light to a different wavelength?
While this isn’t a full explanation, here is a 55 second clip of David Schmidt (inventor of Lifewave patches) giving some more details:
What is Regenerative Medicine?
Short answer: Using the human body’s natural healing capabilities to heal itself
Longer answer: An emerging interdisciplinary field of research and clinical applications focused on the repair, replacement or regeneration of cells, tissues or organs to restore impaired function resulting from any cause, including congenital defects, disease, trauma and aging. [1] Mason, C., & Dunnill, P. “A Brief Definition of Regenerative Medicine.” Regenerative Medicine, (2007), 3(1), 1–5.
Lifewave is focused on activating the cells and systems of the human body to govern its own healing process. This is why the body will pick what it sees as the top priority and focus on repairing that first.
Here is a LONG video interview of David Schmidt (inventor of Lifewave patches) during the 2023 Regenerative Medicine Summit:
Can you review all of this for me in a booklet or brochure?
Yes, I have made a booklet and shorter brochure that can help explain this to your clients visually and quickly. I can easily change any of this for you to have more overlap with your specific practice (massage therapy, myofascial release, chiropractic, nutrition, etc.).
I can also change the last page to have your contact information if you are interested in direct selling.
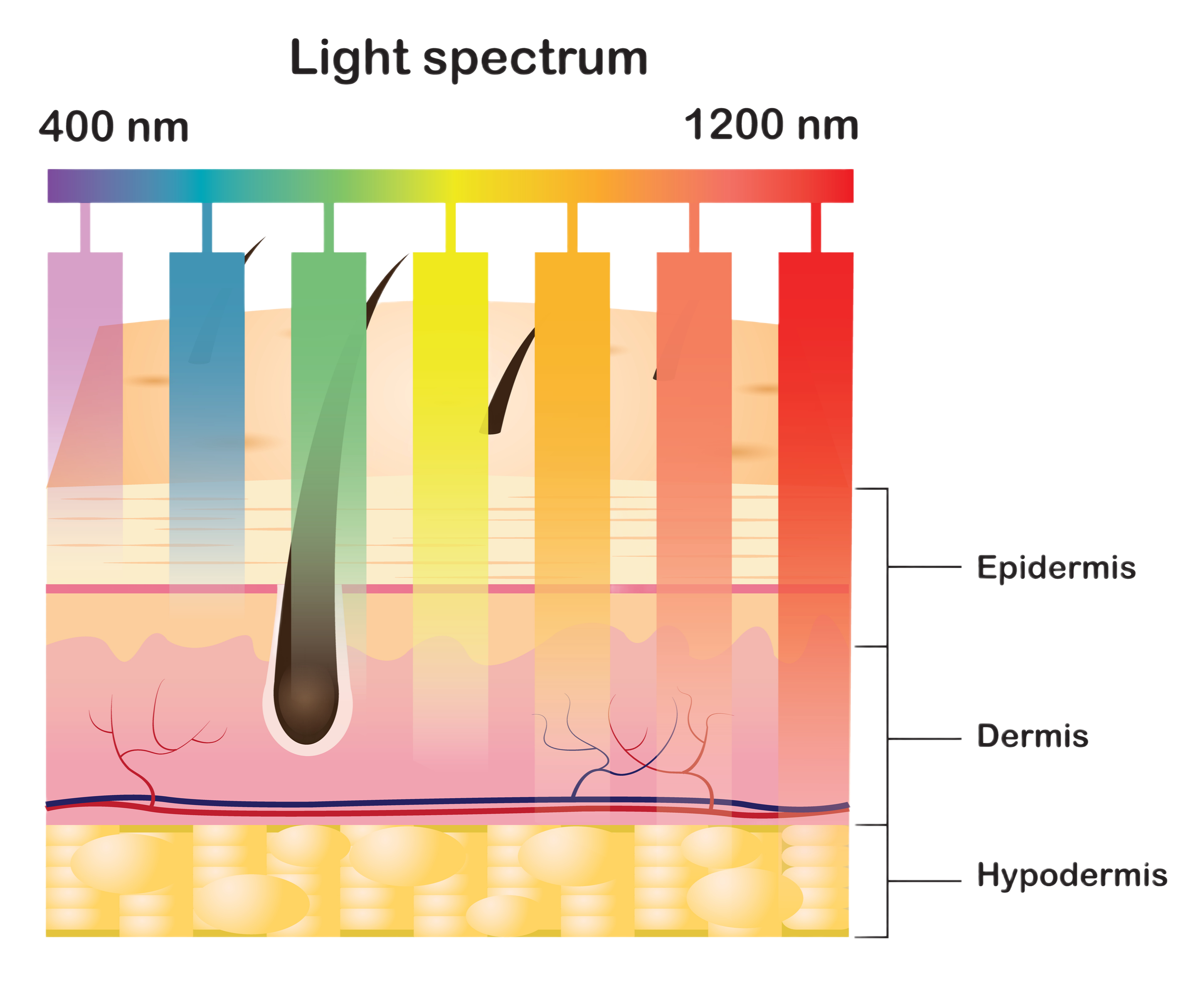
What makes different kinds of phototherapy different?
- Wavelength (or frequency) of light used
- Longer wavelength (or lower frequency) light can penetrate deeper into the body
- 660 nm and 850 nm wavelengths are typically used for red light therapy
- 280 – 315 nm wavelength light is used for UVB (Ultraviolet B) light therapy
- Power of the light source
- sunlight
- LED
- laser light
Other factors :
- Distance from the light source affects the intensity on the skin (1 inch or 3 feet)
- Time of light exposure (30 min. of red light therapy or 5 min. of Laser therapy)
- Frequency of light exposure (1 or 3 times per week)